Intro to Spring Cloud Gateway
本文基于在部门内的一次分享修改而成,主要介绍 Spring Cloud Gateway 的请求处理流程和装配流程。
演示文档是从 markdown 格式文本通过格式转换工具 Pandoc 引用 Reveal.js 转换得到,可供下载。
| Downloads |
|---|
| Markdown |
| Slide |
🔗Intro
🔗Spring Cloud Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective way to route to APIs and provide cross cutting concerns to them such as: security, monitoring/metrics, and resiliency.
简而言之,Spring Cloud Gateway 是一个基于 Java 的 Api 网关系统,开箱即用;如果需要自定义也是可以快速搞定。
文档地址:Documentation 2.1.0 Current GA
🔗pom
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-boot.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>
🔗Spring Reactor
Project Reactor 是 Spring Gateway 的底层技术。其号称是一个 异步反应式的编程模式,竞争者是大名鼎鼎的 RxJava。
Reactor is a fourth-generation Reactive library for building non-blocking applications on the JVM based on the Reactive Streams Specification.
Mono<T>类似于CompletableFuture<T>,支持异步 0/1 个结果或异常的语义Flux<T>类似于Stream<T>,支持异步 N 个结果或异常的语义
🔗Mono
First 构建
Mono<Void> mono = Mono.fromRunnable(() -> dao.update(user));
or
Mono<User> mono = Mono.fromCallable(() -> dao.findById(1000L);
Then 拼接与转换
mono.map(user -> user.getId());
or
mono.flatMap(user -> userDao.deleteById(user.getId());
Finally 异步处理结果
mono.subscribe( value -> System.out.println(value), ex -> ex.printStackTrace(), () -> System.out.println("No data") );
🔗Flux
First 构建
Flux<User> flux = Flux.create(sink -> { final User[] users = userDao.findByName(name); if (users != null) { for (User user : users) { sink.next(user); } sink.complete(); } else { sink.error( new IllegalStateException( "Invalid name: " + name)); } });
or
Flux<String> flux = Flux.just("123", "456", "789");
Then 拼接与转换
flux.map(str -> Longs.tryParse(str));
or
flux.flatMap(user -> userDao.deleteById(user.getId()));
Finally 异步处理结果
mono.subscribe( value -> System.out.println(value), ex -> ex.printStackTrace(), () -> System.out.println("No data") );
🔗WebFlux
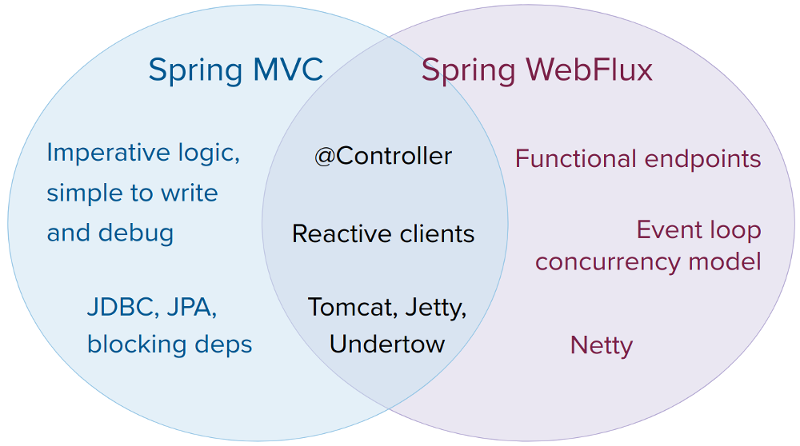
Spring WebFlux - Web on Reactive Stack 是 Spring 推出的基于 Project Reactor 的 HTTP 网络开发框架,相似者是 Vert.x-Web。
fully non-blocking, supports Reactive Streams back pressure, and runs on such servers as Netty, Undertow, and Servlet 3.1+ containers.
- the Spring WebFlux framework
- the reactive WebClient
- support for testing
- and reactive libraries.
WebFlux 被设计来取代或者说补充原有的基于 Servlet 的网络框架:Spring Web MVC - Web on Servlet Stack。
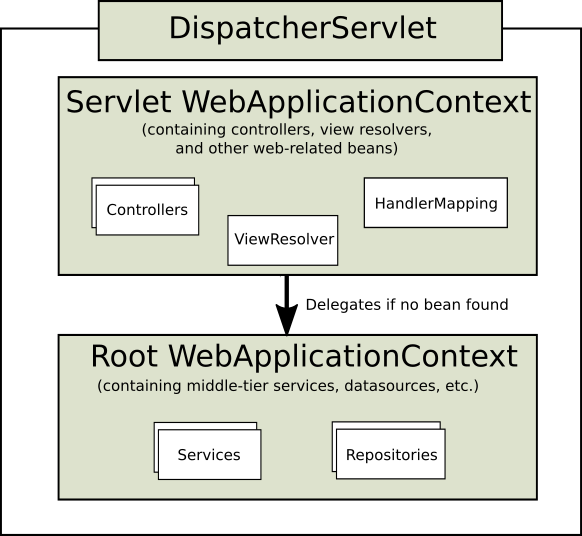
二者的关系:
WebFlux 的典型代码:
@RequestMapping("/root") @RestController public class WebFluxTestController { @GetMapping("/user/{id}") public Mono<UserDto> getUser(final String id) { return Mono.just(new Foobar()); } }
🔗Gateway
🔗Workflow
官方的请求处理流程图:
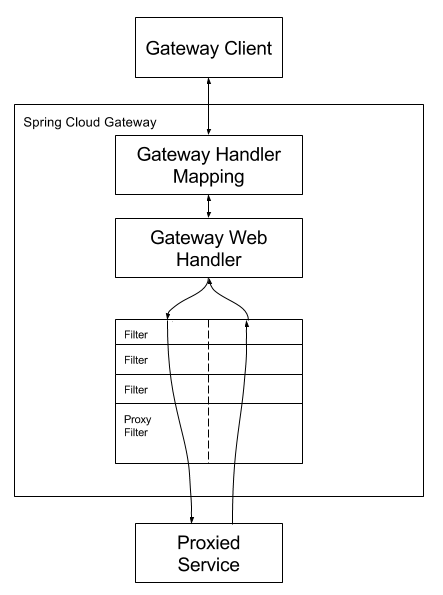
下面来从对象装配(Assembly) 和请求匹配(Runtime) 的角度来深入一下 Spring Gateway 的内部代码。
🔗Assembly - HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration
WebFlux 基于 Spring 的传统对底层的网络层进行了抽象,可以支持 Servlet 的实现和一个内建的 基于 Netty 的实现。Spring Gateway 默认使用基于 Netty 的实现。
首先定位到网络服务器 WebServer 接口的 Netty 实现类。
org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.netty.NettyReactiveWebServerFactory#getWebServerorg.springframework.boot.web.embedded.netty.NettyWebServer#startorg.springframework.http.server.reactive.ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter#applyorg.springframework.http.server.reactive.HttpHandler#handle
发现请求的处理类是 HttpHandler 类。
🔗Assembly - HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration
然后根据 Spring boot 启动逻辑找到 HttpHandler 的实现类。
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ DispatcherHandler.class, HttpHandler.class }) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(HttpHandler.class) @AutoConfigureAfter({ WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class }) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10) public class HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration { @Configuration public static class AnnotationConfig { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public AnnotationConfig(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } @Bean public HttpHandler httpHandler() { return WebHttpHandlerBuilder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext).build(); } } }
定位到 WebHttpHandlerBuilder 类,下一步需要去看看其 build() 方法里面的代码。
🔗Assembly - WebHttpHandlerBuilder
public static final String WEB_HANDLER_BEAN_NAME = "webHandler"; private WebHttpHandlerBuilder(WebHandler webHandler, @Nullable ApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.webHandler = webHandler; // HERE this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public static WebHttpHandlerBuilder applicationContext(ApplicationContext context) { WebHttpHandlerBuilder builder = new WebHttpHandlerBuilder( context.getBean(WEB_HANDLER_BEAN_NAME, WebHandler.class), context); // HERE // ... return builder; } public HttpHandler build() { WebHandler decorated = new FilteringWebHandler(this.webHandler, this.filters); // HERE decorated = new ExceptionHandlingWebHandler(decorated, this.exceptionHandlers); // HERE HttpWebHandlerAdapter adapted = new HttpWebHandlerAdapter(decorated); //HERE // ... return adapted; }
找到了比较关键的 HttpWebHandlerAdapter 类和 FilteringWebHandler 类。
🔗Assembly - HttpWebHandlerAdapter
发现 HttpWebHandlerAdapter 类的逻辑就是把请求转给了 FilteringWebHandler 类。
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) { // ... return getDelegate().handle(exchange) // HERE .doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logResponse(exchange)) .onErrorResume(ex -> handleUnresolvedError(exchange, ex)) .then(Mono.defer(response::setComplete)); }
🔗Assembly - ExceptionHandlingWebHandler
这是 WebHttpHandlerBuilder#build() 里面发现的 ExceptionHandlingWebHandler 类,可以不用重点关注。
@Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { Mono<Void> completion; try { completion = super.handle(exchange); // HERE } catch (Throwable ex) { completion = Mono.error(ex); } return completion; }
🔗Assembly - FilteringWebHandler
重点看一下 FilteringWebHandler 类的实现。
this.chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(handler, filters); // HERE @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return this.chain.filter(exchange); }
里面把请求转给了 DefaultWebFilterChain 类,这个类一听就是一个类似责任链的设计。
🔗Assembly - DefaultWebFilterChain
@Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return Mono.defer(() -> this.currentFilter != null && this.next != null ? this.currentFilter.filter(exchange, this.next) : this.handler.handle(exchange)); }
这里面又做了一层封装,会调用到 DispatcherHandler 类的实现逻辑。
🔗Assembly - WebFluxConfigurationSupport
DispatcherHandler 类在 org.springframework.web.reactive.config.WebFluxConfigurationSupport 中被
自动注册。
@Bean public DispatcherHandler webHandler() { return new DispatcherHandler(); }
🔗Assembly - DispatcherHandler
这个 org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler 又做了一层封装,底下是一系列的
HandlerMapping 类的实现。
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { Map<String, HandlerMapping> mappingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors( context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); ArrayList<HandlerMapping> mappings = new ArrayList<>(mappingBeans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(mappings); this.handlerMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappings); } @Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { if (this.handlerMappings == null) { return createNotFoundError(); } return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) .next() .switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError()) .flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) .flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result)); }
🔗Assembly - RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
HandlerMapping 也是通过 Spring 自动管理的,其实现类是 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.RoutePredicateHandlerMapping。
装配代码在 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayAutoConfiguration 中。
@Configuration @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.cloud.gateway.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) @EnableConfigurationProperties @AutoConfigureBefore({ HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class }) @AutoConfigureAfter({ GatewayLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration.class, GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguration.class }) @ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherHandler.class) public class GatewayAutoConfiguration { @Bean public RoutePredicateHandlerMapping routePredicateHandlerMapping( FilteringWebHandler webHandler, RouteLocator routeLocator, GlobalCorsProperties globalCorsProperties, Environment environment) { return new RoutePredicateHandlerMapping(webHandler, routeLocator, globalCorsProperties, environment); } @Bean @Primary // TODO: property to disable composite? public RouteLocator cachedCompositeRouteLocator(List<RouteLocator> routeLocators) { return new CachingRouteLocator( new CompositeRouteLocator(Flux.fromIterable(routeLocators))); } @Bean public FilteringWebHandler filteringWebHandler(List<GlobalFilter> globalFilters) { return new FilteringWebHandler(globalFilters); } }
GatewayAutoConfiguration 这个装配类里面还提供了 RouteLocator 和 FilteringWebHandler 的实现,这
个后面会用到。
🔗Runtime - RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 中首先从 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator 中去
获取当前所有可用的 Route 实例并找到第一个能匹配当前请求的 Route 放到请求的上下文中,然后调用 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.FilteringWebHandler 里面的代码。
protected Mono<Route> lookupRoute(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return this.routeLocator.getRoutes() // individually filter routes so that filterWhen error delaying is not a // problem .concatMap(route -> Mono.just(route).filterWhen(r -> { // add the current route we are testing exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR, r.getId()); return r.getPredicate().apply(exchange); }) // ... }
RouteLocator 的逻辑后面再讲,先看看 FilteringWebHandler 的逻辑。
🔗Runtime - FilteringWebHandler
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { Route route = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR); List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = route.getFilters(); List<GatewayFilter> combined = new ArrayList<>(this.globalFilters); combined.addAll(gatewayFilters); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(combined); return new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange); }
FilteringWebHandler 中首先从请求的上下文中取出匹配到的 Route 实例,将实例里面的 GatewayFilter
列表和全局的 GlobalFilter 列表合并排序后放入 DefaultGatewayFilterChain (又是一个责任链)中进行
链式处理。
🔗Runtime - DefaultWebFilterChain
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return Mono.defer(() -> { if (this.index < filters.size()) { GatewayFilter filter = filters.get(this.index); DefaultGatewayFilterChain chain = new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(this, this.index + 1); return filter.filter(exchange, chain); } else { return Mono.empty(); // complete } }); }
DefaultGatewayFilterChain 里面维护了一个 GatewayFilter 的集合和一个标识当前正在处理的元素的索引
,每次调用到一个 GatewayFilter 元素的处理逻辑时创建一个新的指向循成额元素的链,以不可变性保证线程
安全。
🔗Routes
Spring Gateway 向外暴露出来的对象之一是路由(Route) 对象,其根据一个或者一系列的条件来判断 接收到的请求是否能被本路由处理,如果能够处理,则使用内置的一系列局部过滤器和全局的过滤器处理请求并返回响应。
🔗Class Route
Route 类的全称是 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.Route,是 Spring Gateway 暴露
出来的处理请求的基本单元。
结构如下:
public class Route implements Ordered { private final String id; private final URI uri; private final int order; private final AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate; private final List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters; // ... }
主要成员是一个请求的判定器 predicate、多个处理器 gatewayFilters、一个后端访问地址 uri,以及一
个唯一标识和序号。
🔗Interface RouteLocator
Spring Gateway 通过 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator 来进行所有路由
对象的加载。
public interface RouteLocator { Flux<Route> getRoutes(); }
🔗RouteLocator Implementations
RouteLocator 接口有以下自带实现:
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CachingRouteLocatororg.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CompositeRouteLocatororg.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator
在 GatewayAutoConfiguration 中可以了解加载的实例:由 RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 管理的路由和多个由第三方自己实现的 RouteLocator 管理的路由被 CompositeRouteLocator 组合起来之后的结果再经过 CachingRouteLocator 被缓存使用。
所有 能被 Spring 感知到的 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator bean 实例都会被默认收集被 CompositeRouteLocator 管理。
🔗RouteDefinitionRouteLocator
RouteDefinitionLocator 用来管理反序列化生成的路由。
@Override public Flux<Route> getRoutes() { return this.routeDefinitionLocator.getRouteDefinitions().map(this::convertToRoute) .map(route -> { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("RouteDefinition matched: " + route.getId()); } return route; }); }
可以看到,其使用了 RouteDefinitionLocator 来管理路由的定义对象,并提供了路由定义对象到路由对象的转
换。
RouteDefinitionLocator 的设计模式与 RouteLocator 相似。
🔗RouteDefinitionLocator and Implementations
package org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route; public interface RouteDefinitionLocator { Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions(); }
RouteDefinitionLocator 的实现类有:
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CompositeRouteDefinitionLocatororg.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocatororg.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository
🔗RouteDefinitionLocator Loading
类似地,在 GatewayAutoConfiguration 中可以找到 RouteDefinitionLocator 被加载使用的逻辑。
@Bean @Primary public RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator( List<RouteDefinitionLocator> routeDefinitionLocators) { return new CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator( Flux.fromIterable(routeDefinitionLocators)); }
所有 能被 Spring 感知到的 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionLocator bean 实例都会被默认收集被 CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator 管理。
🔗RouteDefinition
RouteDefinition 是 Route 路由对象的序列化对象;一个合法的 RouteDefinition 对象可以被构造为一个
路由对象。
public class RouteDefinition { @NotEmpty private String id = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); @NotEmpty @Valid private List<PredicateDefinition> predicates = new ArrayList<>(); @Valid private List<FilterDefinition> filters = new ArrayList<>(); @NotNull private URI uri; private int order = 0; // ... }
与 Route 类似,RouteDefinition 的主要成员是多个请求的判定器定义对象 predicates、多个处理器定义对象 filters、一个后端访问地址 uri,以及一个唯一标识和序号。
🔗Route Construction
所以,Spring Gateway 官方提供了两种方式生成一个路由对象。
🔗Via RouteLocatorBuilder in Java
RouteLocatorBuilder 可以很容易地被用来构建路由对象。
@Bean RouteLocator constantRouteLocator(final RouteLocatorBuilder builder) { return builder.routes() .route("demo_lb", r -> r.header("XHOST") .filters(f -> f.prefixPath("/search")) .uri("lb://httpbin.org")) .build(); }
🔗Via RouteDefinition in YAML/Properties
RouteDefinition 可以很容易地被用来从外部配置文件 (YAML/Properties) 构建路由对象。
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: r1 order: 2 uri: "https://a.com" predicates: - host=a.org filters: - AddRequestHeader=XHOST,my.a.org - id: r2 order: 1 uri: "https://b.com" predicates: - Host=b.org filters: - AddRequestHeader=XHOST,my.b.org
🔗Predicate
谓词对象即路由对象里面的判定条件。
🔗AsyncPredicate
Route 类里面的谓词对象的类型是 AsyncPredicate。
public class Route implements Ordered { private final String id; private final URI uri; private final int order; private final AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate; // HERE private final List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters; // ... }
🔗PredicateDefinition
相比 AsyncPredicate 类,我们更关心其对应的定义类 PredicateDefinition。
public class PredicateDefinition { @NotNull private String name; private Map<String, String> args = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // ... }
为了保持代码简单,其定义被设计为一个类型标识名和一个 K-V 的映射表。
🔗PredicateDefinition to AsyncPredicate
PredicateDefinition 到 AsyncPredicate 的转换逻辑在 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 类的 lookUp 方法里面,大量使用了反射的技巧。
其中,使用了 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.RoutePredicateFactory 类作为二者
转换的桥。
🔗RoutePredicateFactory
该类全称 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.RoutePredicateFactory<C>,提供了一个
统一的基于 Spring 通用反射模式的谓词构造工厂类。
public interface RoutePredicateFactory<C> extends ShortcutConfigurable, Configurable<C> { AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> applyAsync(Consumer<C> consumer); Class<C> getConfigClass(); }
🔗Builtin Predicate Factories
官方默认提供了以下谓词构造工厂的实现类,可以实现多种不同的请求匹配能力。
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.AfterRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.BeforeRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.BetweenRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.CookieRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.HeaderRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.HostRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.MethodRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.PathRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.QueryRoutePredicateFactoryorg.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.RemoteAddrRoutePredicateFactory
🔗Filter
过滤器对象即路由对象中匹配后处理逻辑的封装。
🔗GatewayFilter
Route 类里面的过滤器对象的类型是 GatewayFilter。
public interface GatewayFilter extends ShortcutConfigurable { Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain); }
该类与之前的 DefaultGatewayFilterChain 类结合起来,组成了一个链式的请求处理流程。
🔗FilterDefinition
相比 FilterDefinition 类,我们更关心其对应的定义类 FilterDefinition。
public class FilterDefinition { @NotNull private String name; private Map<String, String> args = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // ... }
为了保持代码简单,其定义被设计为一个类型标识名和一个 K-V 的映射表。
🔗FilterDefinition to GatewayFilter
从定义生成过滤器对象的逻辑在 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 的 loadGatewayFilters 方法中。其中,同样使用了 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.GatewayFilterFactory 类作为二者转换的桥。
🔗GatewayFilterFactory
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.factory.GatewayFilterFactory<T> 的设计模式和使用方式同
RoutePredicateFactory 。
public interface GatewayFilterFactory<C> extends ShortcutConfigurable, Configurable<C> { default GatewayFilter apply(Consumer<C> consumer) { C config = newConfig(); consumer.accept(config); return apply(config); } default Class<C> getConfigClass() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("getConfigClass() not implemented"); } }
🔗Builtin Filter Factories
官方默认提供了以下过滤器构造工厂的实现类,可以实现多种不同的请求处理能力。
- AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter Factory
- AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- Hystrix GatewayFilter Factory
- FallbackHeaders GatewayFilter Factory
- PrefixPath GatewayFilter Factory
- PreserveHostHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- RequestRateLimiter GatewayFilter Factory
- RedirectTo GatewayFilter Factory
- RemoveNonProxyHeaders GatewayFilter Factory
- RemoveRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- RemoveResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- RewritePath GatewayFilter Factory
- RewriteResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- SaveSession GatewayFilter Factory
- SecureHeaders GatewayFilter Factory
- SetPath GatewayFilter Factory
- SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- SetStatus GatewayFilter Factory
- StripPrefix GatewayFilter Factory
- Retry GatewayFilter Factory
- RequestSize GatewayFilter Factory
- Modify Request Body GatewayFilter Factory
- Modify Response Body GatewayFilter Factory
🔗Global Filter
全局过滤器对象是对路由反向代理到后端能力的封装,其主要通过 URI 的 scheme 来决定应用的逻辑;一般来说 ,不同的 scheme 会有不同的全局过滤器对象来处理。
当前官方默认能支持的 scheme 有:
- http
- https
- lb
- forward
全局过滤器的接口同普通过滤器,但没有提供从定义反序列化生成的能力。
以上。